RUBY
Ruby is a deep red colored gemstone only second in popularity for colored stones. Rubies, scientifically known as corundum, are a natural Gemstone mined from the Earth and derive their color from natural trace elements like Chromium. Rubies are typically mined from Madagascar, Nepal, Thailand and Australia. Rubies are most commonly used in jewelry, specifically in right hand rings and earrings. They are also very popular in the US as a July birthstone and for the 40th milestone anniversary. Rubies are best set in white and yellow gold because their color is brightened and accentuated. There are a variety of popular Ruby shapes, most notably round cut and oval cut. Rubies are unlike diamonds in that there is no grading standardization. The most important factors in determining the quality and price of a Ruby is it’s size, color and clarity, with color being the most critical factor in setting the grade

Ruby Shape
Rubies are available in almost all shapes, however some shapes are most popular because they bring out the red color more vibrantly. Round rubies are most popular. They are commonly used in solitaire rings, earrings and as accent stones in wedding / right hand bands. The second most popular shape is the Oval Ruby. Oval rubies reduce rough wastage and draw out the deep red color and so cutters prefer the Oval shape. Other popular shapes include Emerald/Octagon and Heart shape (a red heart is of course a symbol of love and affection). In large sizes above 6mm or approximately 1.00ct, the cushion is more common and popular. In smaller sizes below 4mm or approximately 0.30ct, the Princess/Square shape is popular. Round rubies tend to have the most sparkle because their faceting allows light to reflect and bounce a red sparkle back to the eye. Because of the light reflection, it is important to have more color in the round Ruby. Other fancy shapes are deport in cut and so the color is more relevant than the sparkle. Shape rarely affects the visibility of clarity inclusions in Rubies.
Ruby Color
The most important characteristic of a Ruby is its color. Color is judged by three main criteria: hue, tone and saturation. Hue is the physical color of the Ruby. Is it red, or pink or somewhere in between. Tone is the depth of color. Is it dark, light or again, in between. Saturation is the evenness and distribution of color. Is it an even color throughout or are there lighter or dark patches visible. Ruby color is ideally a rich, deep even and vivid red color. That doesn’t mean a light or darker red Ruby is a bad thing – simply that the most valuable or expensive rubies have a “blood red” color. Rubies, and most other gemstones, are not graded with magnification. The reason is that the deep color is the priority and the color often masks inclusions, therefore magnification is not required. When examining color, place the Ruby face up, between 2 fingers or on a white surface and rock and tilt the Ruby to examine color from several angles. Your eyes and innate instincts are very good at judging color so you’ll very easily be able to determine the quality.
Rubies are graded on a scale unlike diamonds. The industry wide Ruby scale is below, along with the corresponding colors required to achieve that grade. Please note that the grading system for gemstones is quite arbitrary and laboratories do not assign a grade to the Ruby color. Because every Ruby is distinct and so different from one another, it is impossible to standardize the grading scale.
The pricing varies based on color. It is important to note that color (apart) from size, is the single biggest price factor. Additionally, because an A quality Ruby can be very dark or very light, the price may be similar. The tone isn’t the only determining factor. All three, hue, tone and saturation, must be evaluated together when pricing a Ruby.
Ruby Size
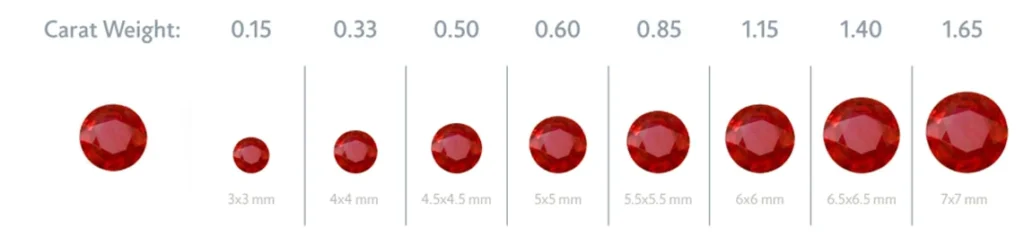
Rubies are often calibrated and cut to specific millimeter measurement requirements, based on the Ruby shape. Rubies should not be compared to diamond as they tend to be deeper in all shapes and so a Ruby’s carat weight will rarely ever match a diamond’s carat weight, if the measurements are the same. A 1.00ct Round Ruby is closer to 6mm; whereas a 1.00ct Round Diamond is about 6.4mm. A Gemstone manufacturer’s goal is to reduce rough wastage and to preserve carat weight. Therefore, Rubies are cut in different shapes and sizes. There is not standard uniform cutting practice in terms of the number of facets. It is imperative to understand the millimeter dimensions on the Ruby, rather than the carat weight. Like with all gemstones, the larger the Ruby, the rarer and more expensive. The prices change exponentially, not in a linear fashion.
Below are examples of each Ruby shape and the typical millimeter measurements and approximate corresponding carat weights.
Ruby Clarity
The formation of rubies requires a lot of Earth’s natural elements and many years of pressure and natural growth. This growth process incorporates many of the earth’s elements, which can affect the clarity of the stone. During their growth process, rubies will develop fractures and inclusions that affect the color and visibility.
Many of the inclusions you see in diamonds can also be seen in rubies. Rubies possess clouds, needles, feathers, crystals, pinpoints, etc. All Rubies have inclusions and the severity of those inclusions affects the ruby color and visibility. Rubies with many inclusions will look, dull in color and sparkle. They will look, whitish or pinkish and opaque. As the number and severity of inclusions decreases the color looks brighter, deeper and more even. With Clarity selects rubies with minimally visible inclusions, hence our AAA quality.
Inclusions are graded face up without magnification. The inclusions are mostly measured by their impact on color so it isn’t necessary to magnify and look for them. Additionally color can help mask inclusions as well. Therefore, they’re not graded the same way as they are with diamonds. Their pricing is also similar to the way color is graded. The higher the clarity and color combination, the more exponentially valuable the ruby becomes.

Ruby Sourcing
Ruby is mined from a variety of countries rich in minerals and natural resources. Rubies do require special subterranean conditions, unlike diamonds which can be found almost anywhere. With Clarity rubies are sourced from Myanmar, Australia, Madagascar and Thailand. While rubies can be found in other countries as well, we work with suppliers and mines from these nations because of their commitment to supporting no conflict mining and community development practices.
Rubies are a rich mineral and Ruby mining creates many jobs, infrastructure and funds hospitals, schools and community centers. Our Rubies come from no conflict zones. We work closely with suppliers to ensure that best environmental practices are followed. We do this by verifying the Mine locations and have visited many of our sources.
Rubies are generally much more scarce than diamonds. Their scarcity makes it too difficult to deploy as a conflict mineral. Rubies are an optimal choice in engagement rings and other jewelry for anyone concerned about conflict minerals.
Ruby Certification
Colored gemstones are typically not certified. The reason is that there are no standardized grading scales or practices that make it consistent to grade. Ruby examination is more of an art than a science. The science purely lies in the identification of treatments and whether it is a natural corundum or lab created.
All With Clarity Rubies are 100% natural gemstones. We do not work with labs to create any of our gemstones and we independently test every ruby with tools in our gemologist offices. That’s our promise. No matter which jeweler you choose, you need to be confident about how they examine their rubies and how they source them.
For large or rare rubies, there are labs that specialize in Ruby grading. This labs include GIA, AGS, and AGL, as far as well reputed go. We recommend certifying rubies above 2.00ct, as the value will prove it worth while. Often times, a more cost effective route will be to have a certified appraiser verify the gemstone. The appraiser will most likely identify the same things the lab will. The one thing though that the lab can tell you is the country of origin. For some, this is important and can actually affect the value of the ruby. Rubies for some countries, such as Myanmar, are more valuable because they are rarer and have more desirable color attributes.
In general, we always recommend natural gemstone as jewelry is a meaningful and emotionally driven purchase. Synthetic gemstones also never look visually as appealing as nature gemstones. Even inclusions, up to a certain extent, also add to the appeal of a ruby. Rubies are like art.
Ruby Treatments
Almost every gem quality ruby will undergo basic or standard treatments that will slightly improve it’s quality. Such treatments include heating, oiling, glass filling. With Clarity will never use glass or lead filled rubies. We believe these are temporary treatments to mask inclusions and can create structural problems in the long term. Untreated natural rubies can be more than 10 times more expensive than treated rubies.
Heating is literally exposing the Ruby to high temperature, which can improve the depth of color. This is a permanent treatment that is required for many Rubies, otherwise the colors would look far too light.
Other treatments include oiling, dyeing, bleaching, waxing, irradiating and laser drilling. With Clarity does not source gemstones that undergo these treatments. Our gemologists examine every Ruby with a microscope and other testing equipment to check for treatments other than heating.

